Storage Spaces Direct is typically run on hardware, but it can also be virtualized. In this guide we are going to create 4 node Storage Spaces Direct cluster inside Hyper-V.
Before we begin
You will usually read that Storage Spaces Direct is run on hardware, but it can also be run inside virtual machines.
It is recommended to run Storage Spaces direct on hardware for production environments, but for myself I find it doable for some non-critical (and light) workloads even in virtualization mode.
Before you begin with Storage Spaces Direct, if you are not sure what it is all about, make sure you start here – https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/storage/storage-spaces/storage-spaces-direct-overview and make yourself comfortable with technology.
This is also a great read – https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/storage/storage-spaces/deploy-storage-spaces-direct
Prerequisites
This will be tutorial for four Hyper-V nodes with four virtual machines. You can also simulate this on one Hyper-V host if you have enough resources (I did this guide on one machine).
Here you can read about hardware requirements (can also be good guide line for virtual environment) https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/storage/storage-spaces/storage-spaces-direct-hardware-requirements
Hyper-V host
On Hyper-V host I created two virtual switches – one is “External” type through which machines communicate with the clients and rest of the network. I unchecked “Allow management operating system to share this network adapter” since I have dedicated network adapter for Hyper-V. In case you have only one network adapter on you Hyper-V host, you should leave that checked, otherwise your host won’t have network connection.
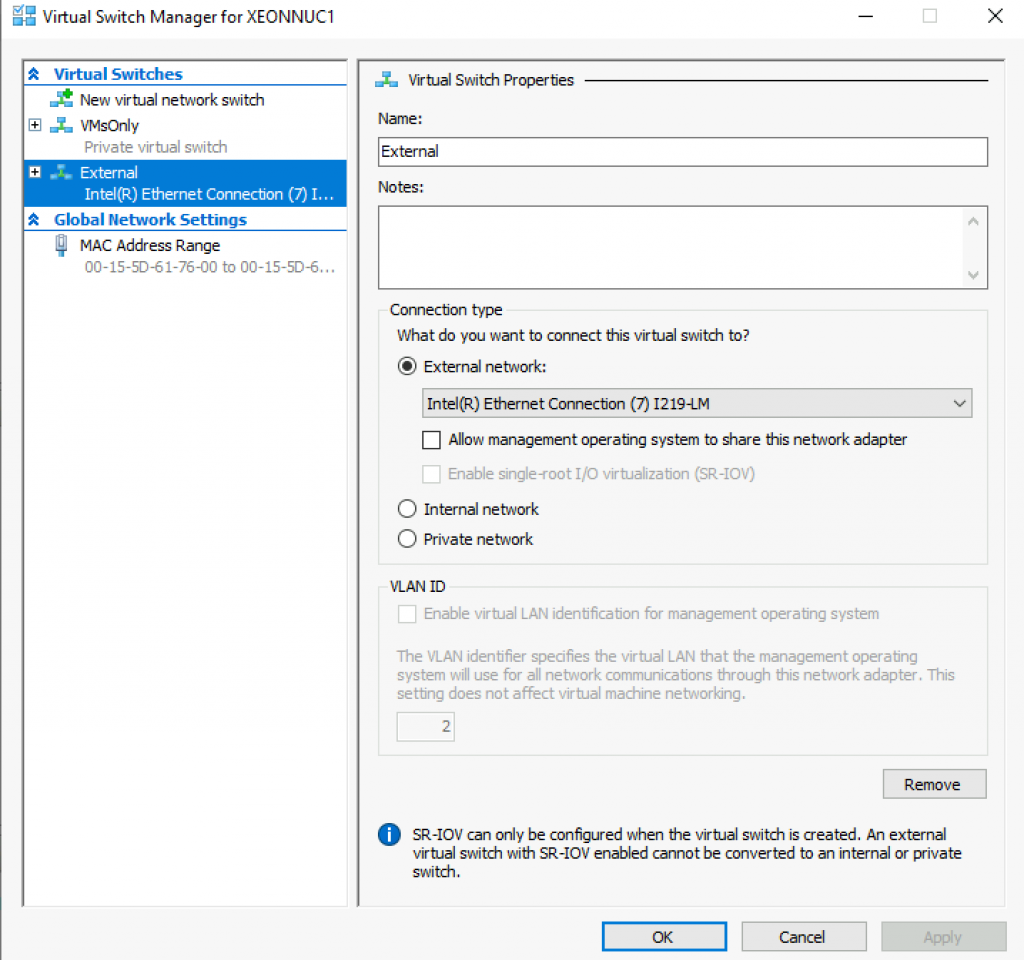
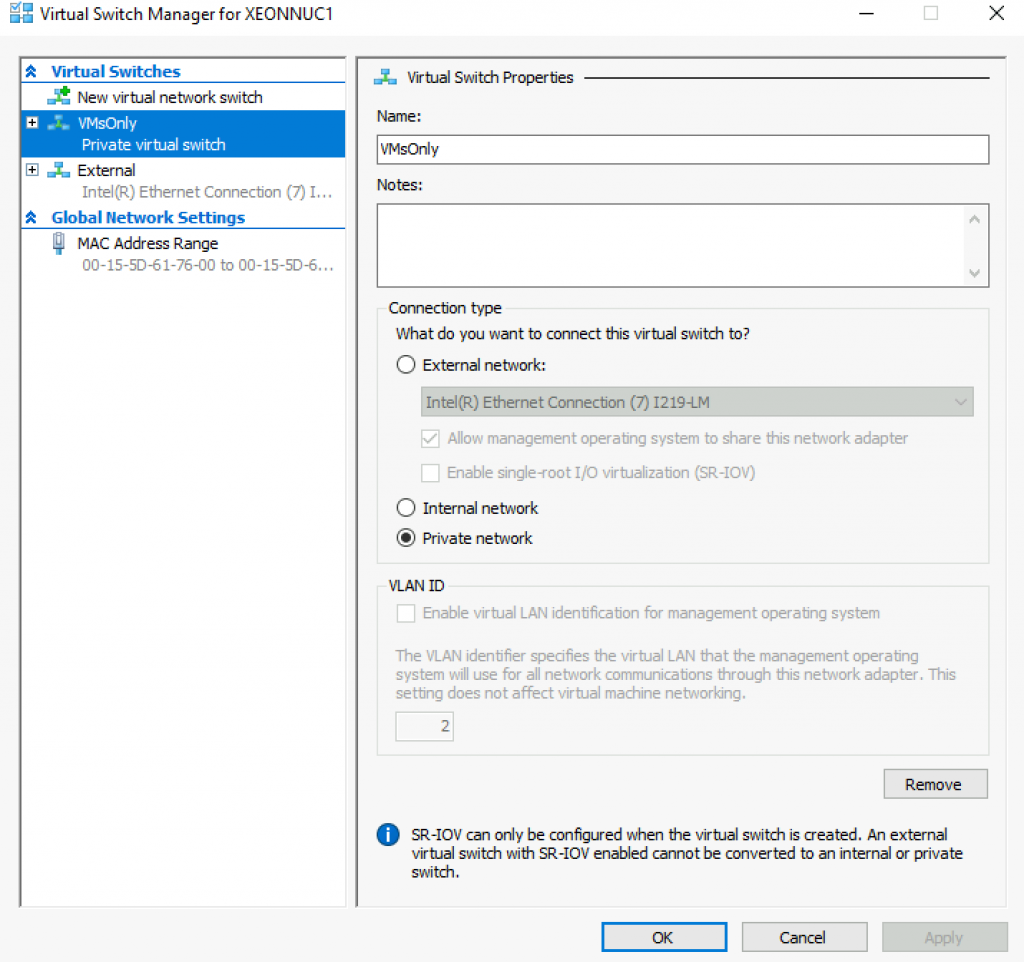
Second one is private (I named it VMsOnly) and it is only for communication between VMs.
I have one VM which serves as domain controller. I named it DC and it has IP address of 10.0.0.31. Domain name is informatiker.local. VM has only one network adapter connected to External network switch.
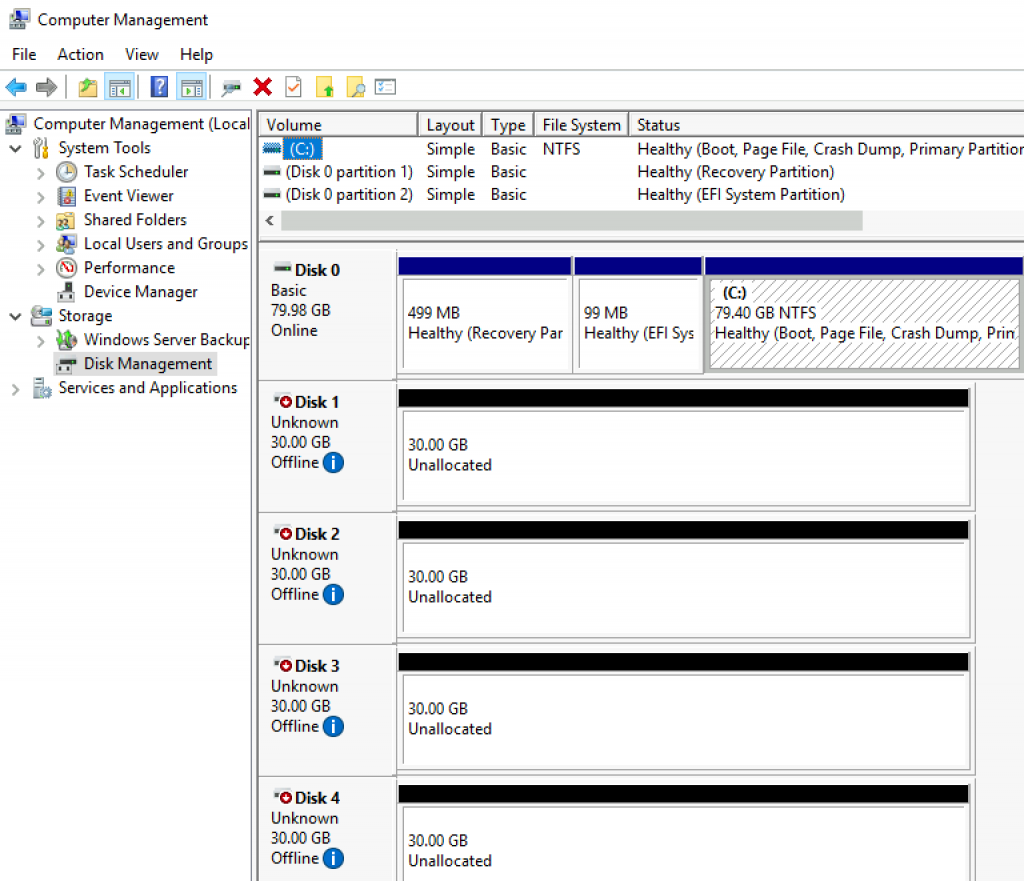
I created four VMs with 4cores, 8GB of RAM, and five disks in total. One for system, and four drives for Storage Spaces Direct (30GB in size, each). Do not initialize or create volumes on four drives for Storage Spaces Direct! You can also attach physical disks directly to your VMs, but in this guide I will use standard vhdx.
Each VM also two network adapters – one network adapter connected to External network switch and another one to private switch (for cluster heartbeat).
I named VMs as follows:
Node1 – External IP 10.0.0.123 Private IP 192.168.5.2
Node2 – External IP 10.0.0.124 Private IP 192.168.5.3
Node3 – External IP 10.0.0.125 Private IP 192.168.5.4
Node4 – External IP 10.0.0.126 Private IP 192.168.5.5
All of the machines should be added to your domain.
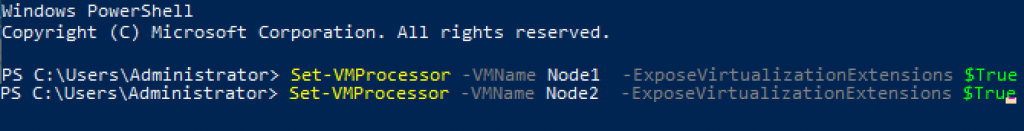
We need to enable nested virtualization on each Hyper-V host on which Storage Spaces Direct will be installed
In my case it is only one host
Set-VMProcessor -VMName Node1 -ExposeVirtualizationExtensions $TrueYou need to run this command for each VM you created.
You will also need to enable MacAddressSpoofing for each of the created VMs.
Get-VMNetworkAdapter -VMName Node1 | Set-VMNetworkAdapter -MacAddressSpoofing On
You can also do this by opening Settings of the VM inside Hyper-V Manager, and going to Network Adapter and extend its properties | Select Advanced Features and click on Enable MAC address spoofing.
Virtual machines
I already written about specs for our four nodes.
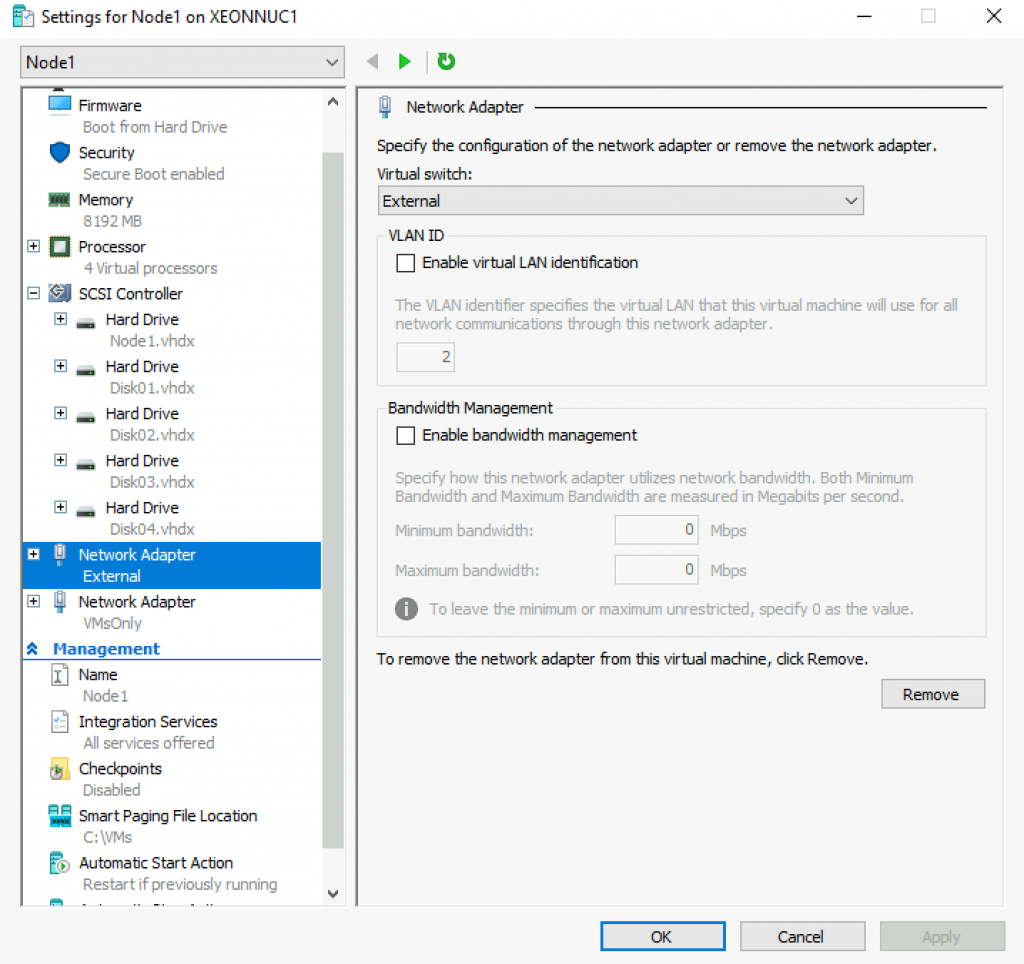
We need to install Windows Server 2019 Datacenter on all of the four nodes.
Also, we will join these machines to our domain.
This is how your disk layout should look like
Install required Roles/Features on the Storage Spaces Direct nodes
On each of the four nodes we will install following roles
Hyper-V, Failover-Clustering, File Server, Data Center Bridging, RSAT Clustering and Hyper-V Powershell.
I also managed to get by with Failover Clustering and File Services installed. You can do this also through Server Manager if you have GUI installed.
Install-WindowsFeature -Name "Hyper-V", "Failover-Clustering", "Data-Center-Bridging", "RSAT-Clustering-PowerShell", "Hyper-V-PowerShell", "FS-FileServer"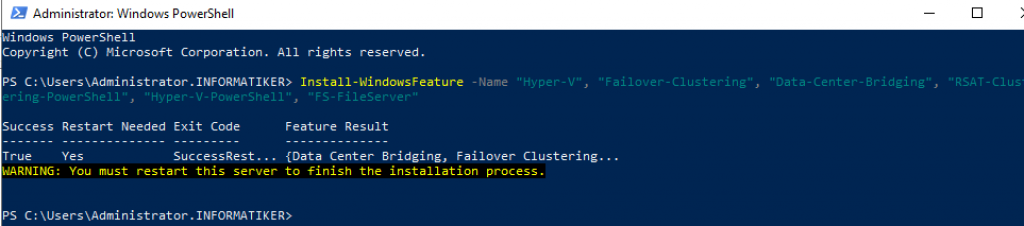
Repeat this install on all four nodes and reboot them.
We will now test if our four nodes are prepared for clustering. I will run this test on Node1 in Powershell as admin.
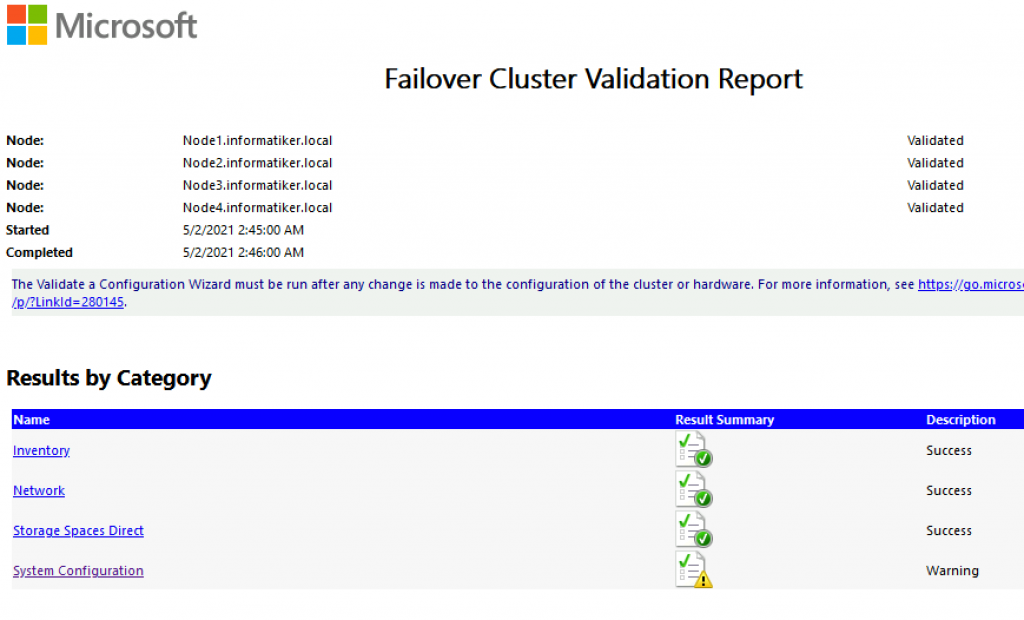
Test-Cluster –Node Node1,Node2,Node3,Node4 –Include "Storage Spaces Direct", "Inventory", "Network", "System Configuration"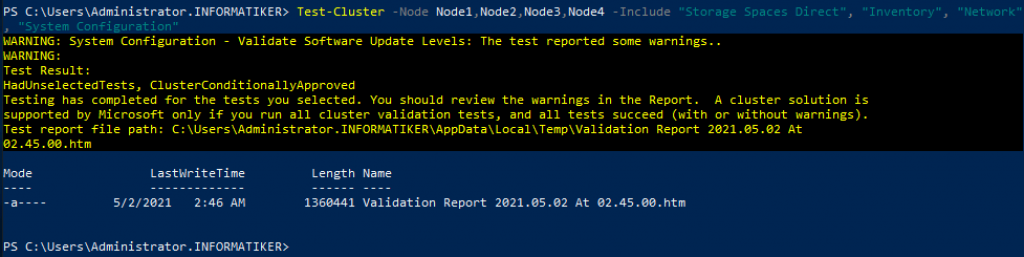
You can also check your results in C:\Users\YourUserName\AppData\Local\Temp\Validation report XY….
If you installed Windows Server with GUI, you may also want to have Failover Cluster Manager installed. To install it, type into powershell
Install-WindowsFeature RSAT-Clustering-MGMTIn case there are no errors, you can proceed. I got a warning inside System Configuration, but nothing special…
Create Storage Spaces Direct Cluster
Ok, if you cleared your cluster test ok, we can go forward. We will now create cluster. I will name my cluster StorCluster, and include all four nodes into it. Also, NoStorage switch is important since this cluster will be used as Storage Spaces Direct cluster. I will also assign IP address to this cluster – 10.0.0.127
I will run this command from Node1.
New-Cluster –Name StorCluster –Node Node1,Node2,Node3,Node4 –NoStorage -StaticAddress 10.0.0.127
If you wish to use this in production, cluster witness may be a good idea. You can look it up here in step 3.4. Deploying cluster witness can help you withstand loosing two nodes for example in our scenario with four nodes.
Here is the script from this link under Section 3.1. It is c/p below. Change Node1, Node2… to the name of your nodes and save it as .ps1 script.
This script will remove all the data from all the disks except OS drive, so be careful when executing it! Make sure your nodes are clean and don’t have any valuable data before you execute this!
# Fill in these variables with your values
$ServerList = "Node1", "Node2", "Node3", "Node4"
Invoke-Command ($ServerList) {
Update-StorageProviderCache
Get-StoragePool | ? IsPrimordial -eq $false | Set-StoragePool -IsReadOnly:$false -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Get-StoragePool | ? IsPrimordial -eq $false | Get-VirtualDisk | Remove-VirtualDisk -Confirm:$false -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Get-StoragePool | ? IsPrimordial -eq $false | Remove-StoragePool -Confirm:$false -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Get-PhysicalDisk | Reset-PhysicalDisk -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Get-Disk | ? Number -ne $null | ? IsBoot -ne $true | ? IsSystem -ne $true | ? PartitionStyle -ne RAW | % {
$_ | Set-Disk -isoffline:$false
$_ | Set-Disk -isreadonly:$false
$_ | Clear-Disk -RemoveData -RemoveOEM -Confirm:$false
$_ | Set-Disk -isreadonly:$true
$_ | Set-Disk -isoffline:$true
}
Get-Disk | Where Number -Ne $Null | Where IsBoot -Ne $True | Where IsSystem -Ne $True | Where PartitionStyle -Eq RAW | Group -NoElement -Property FriendlyName
} | Sort -Property PsComputerName, Count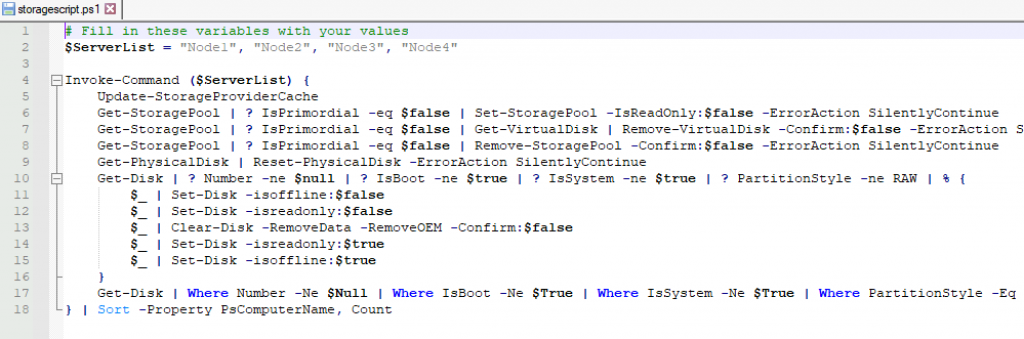
I will run this script in Powershell from Node1. This is the result of my script
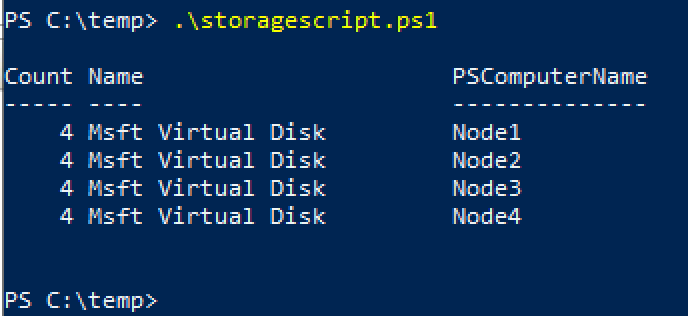
Ok, we can proceed further. Script prepared four disks per node.
Now, we will create Cluster for Storage Direct Spaces. I will run it on Node1 through Powershell as admin.
Enable-ClusterStorageSpacesDirect –CimSession StorCluster
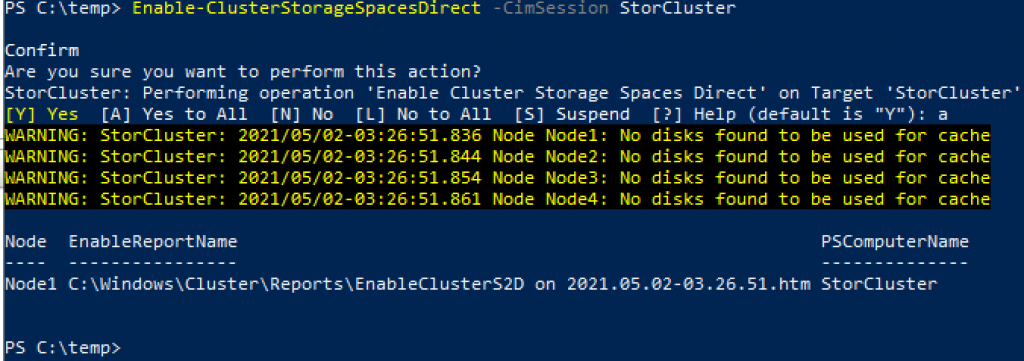
You can ignore warning for cache.
I also installed my servers with GUI for this guide, and Failover Cluster Manager is in place.
Now, if I look into Failover Cluster Manager under Storage | Disks, this is what i see
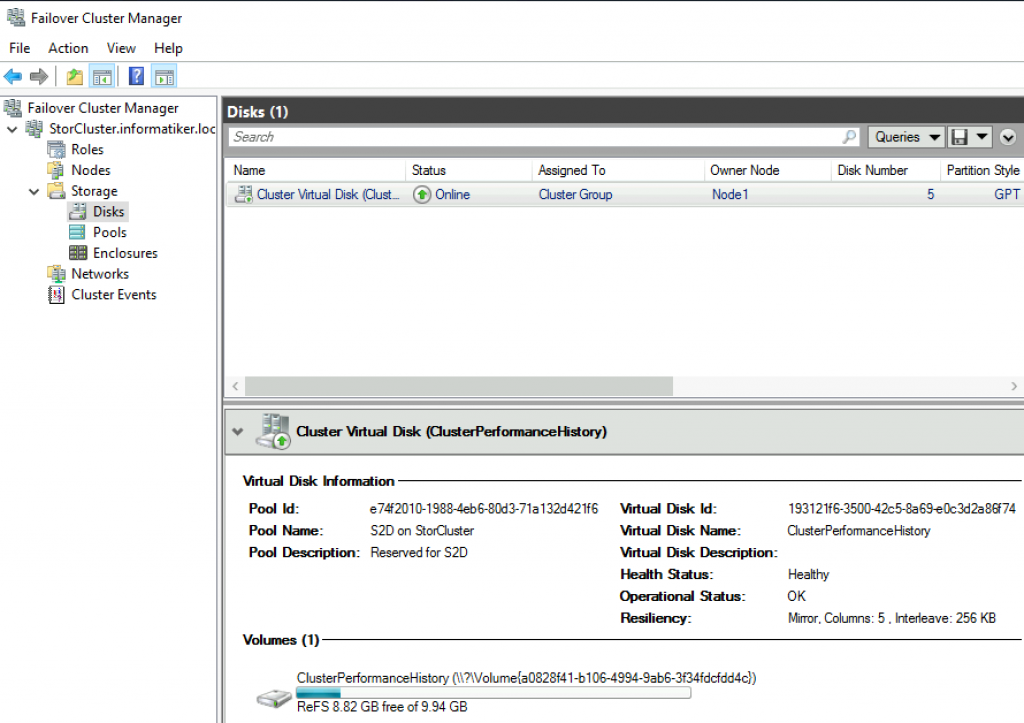
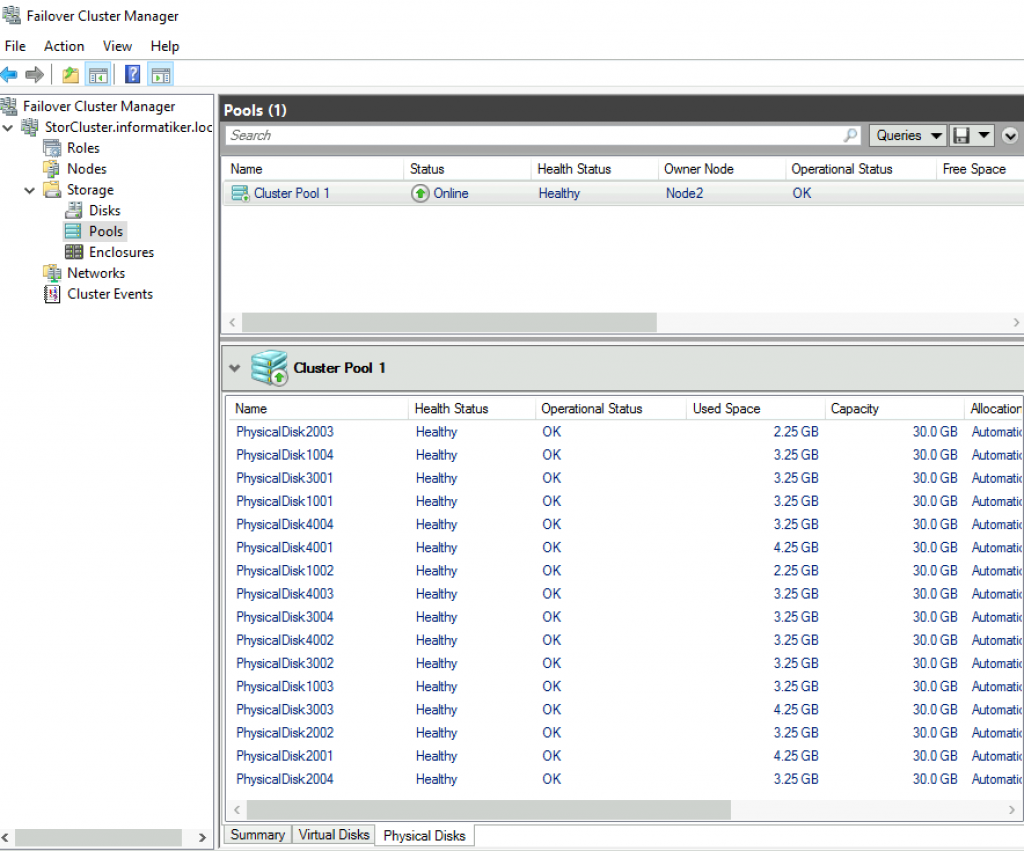
Create Cluster Volume
Ok, this is last part of this process – to create volume. Here you can read more about creating volumes – https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/storage/storage-spaces/create-volumes
and this also is useful page – https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/storage/storage-spaces/plan-volumes
Since we have four nodes we will create following
New-Volume -FriendlyName "Vol1" -FileSystem CSVFS_ReFS -StoragePoolFriendlyName S2D* -Size 68GB -ResiliencySettingName Mirror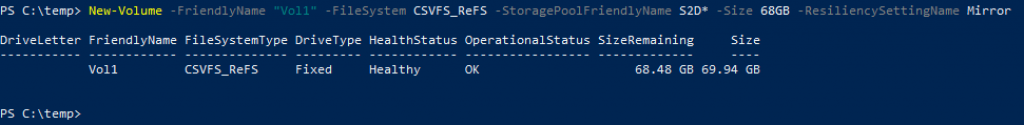
And if we look into Failover Cluster Manager…
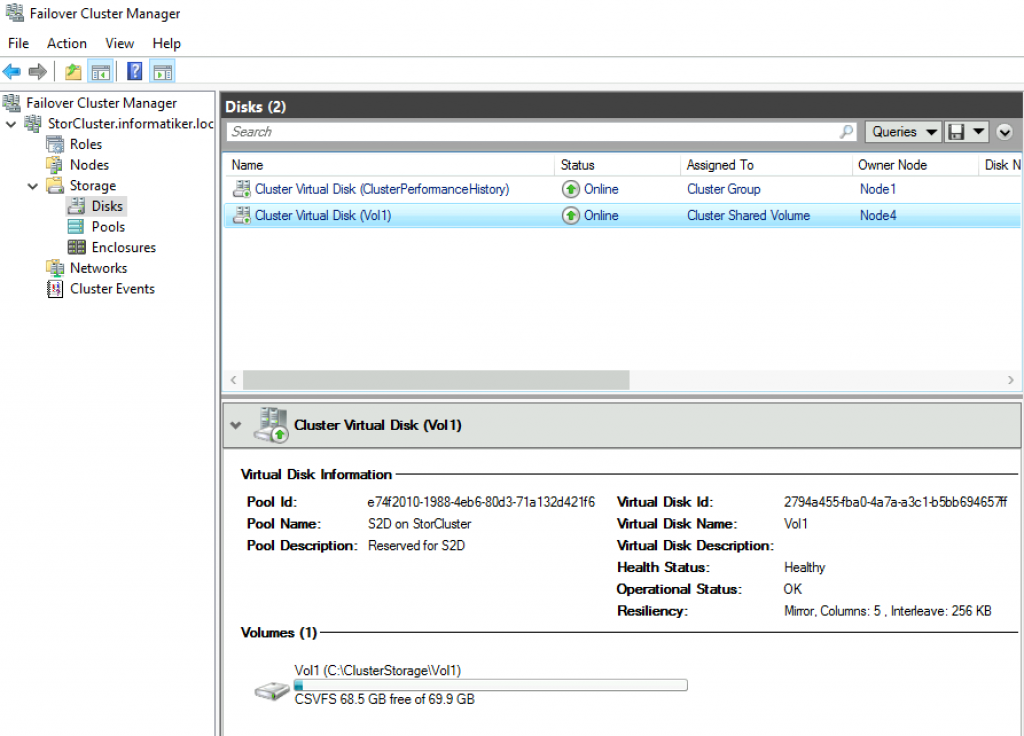
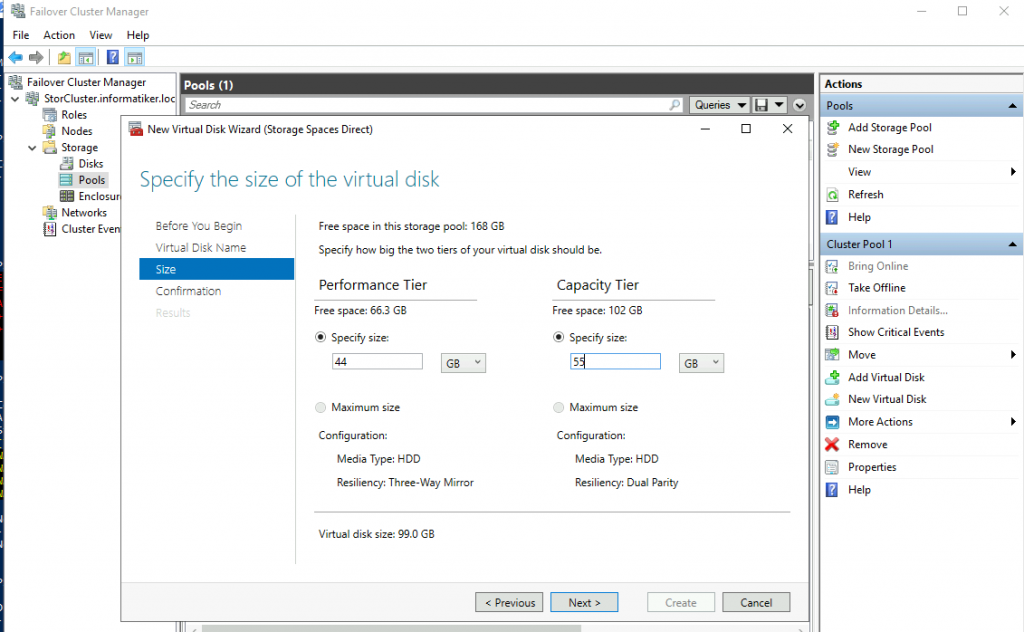
You can also do this through Failover Cluster Manager by going to Storage | Pools | New Virtual Disk.
I will only point out one piece of this wizard – part where you’ll be offered Performance Tier and Capacity Tier – Performance part will be optimized for IO performance (hot storage) while Capacity tier is optimized for storage (cold storage).
That is it for this guide, you now know how to deploy Storage Spaces Direct inside VM.