Another one of quick tutorials, this time on the topic of VNC server on CentOS/RHEL
Prerequisite for the VNC server is GUI interface – GNOME for CentOS 8/RHEL 8.
But, before we start installation procedure, we will check if Wayland display manager is configured as default display manager.
First, we need to change to root by entering following command:
suThen, enter following:
vi /etc/gdm/custom.conf
Wayland should be set to false:
WaylandEnable=false 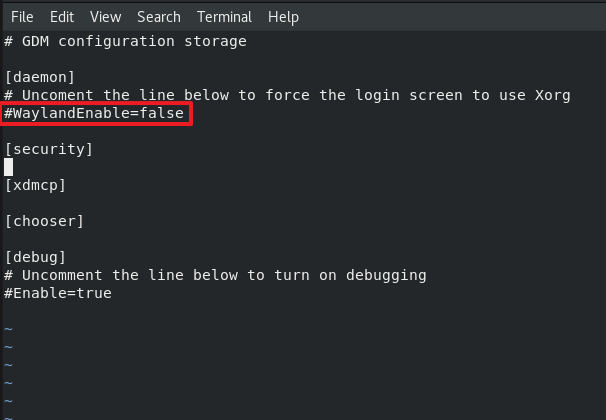
When you are done with editing, quit vi with
:q!Let’s proceed with VNC Server installation
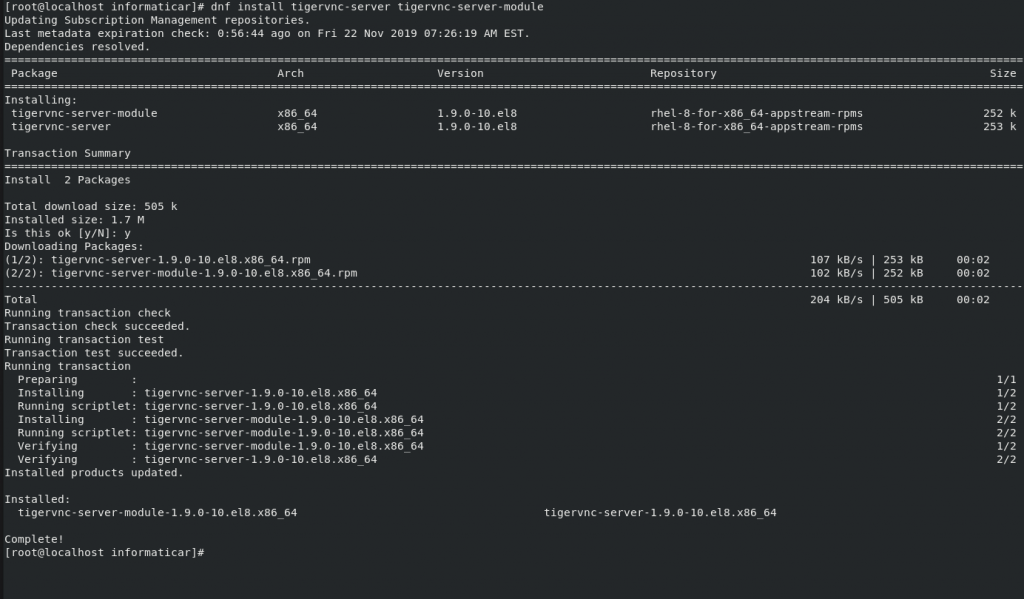
Installation command for TigerVNC is
dnf install tigervnc-server tigervnc-server-module
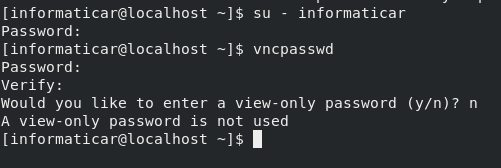
Next we, will switch to user which will use VNC and set VNC server password:
su – informaticar
vncpasswd
Now let’s switch back to root account by running following command:
exit
Next, we will have to configure VNC server. We will create new configuration file vncserver@.service in /etc/system/system/
suThen run following command (file will be opened in vi editor)
vi /etc/systemd/system/vncserver@.service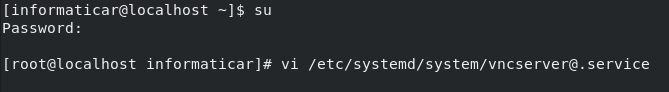
New blank screen will open, and you need to enter following configuration into it (change informaticar with your username)
[Unit]
Description=Remote desktop service (VNC)
After=syslog.target network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
WorkingDirectory=/home/informaticar
User=informaticar
Group=informaticar
PIDFile=/home/informaticar/.vnc/%H%i.pid
ExecStartPre=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :'
ExecStart=/usr/bin/vncserver -autokill %i
ExecStop=/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
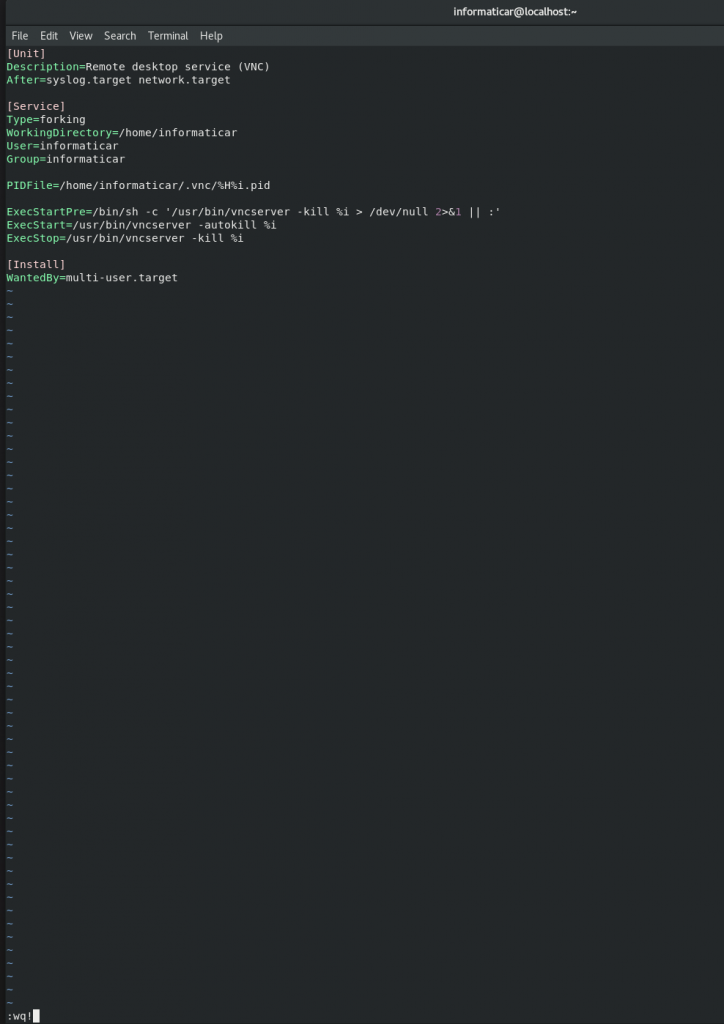
When you are done, type :wq! to save and quit
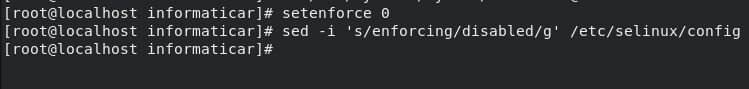
Before starting VNC we need to disable SELinux
setenforce 0
sed -i 's/enforcing/disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
Now, with following commands we will reload VNC server, enable it to start at startup and check if it is up and running
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl start vncserver@:1
systemctl enable vncserver@:1
systemctl status vncserver@:1

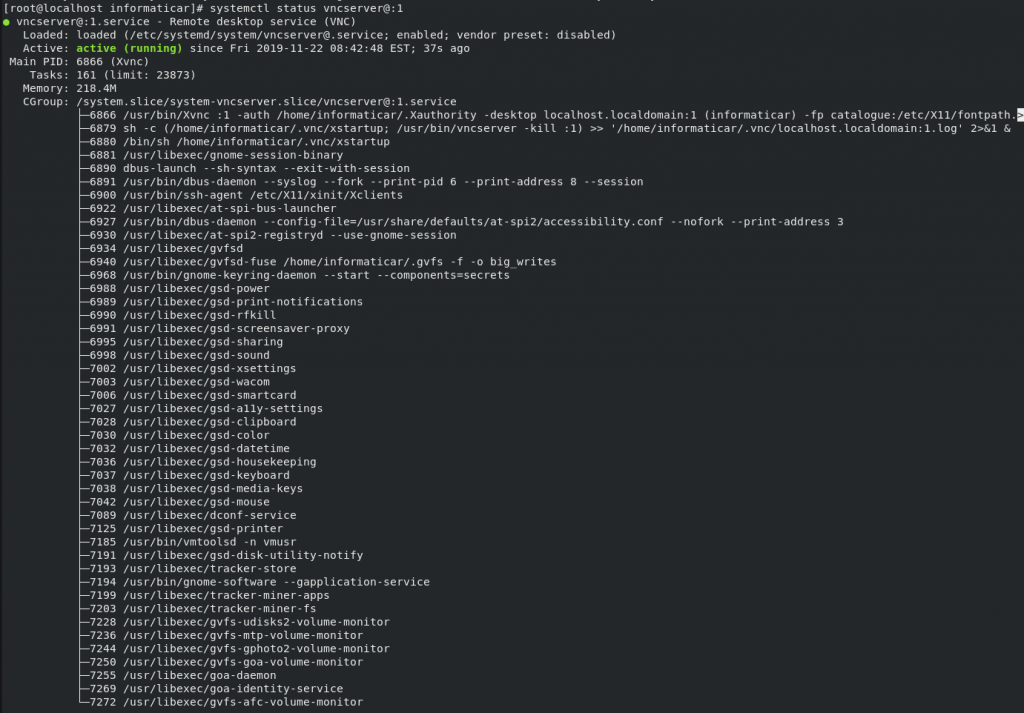
Service is up and running.
Next, lets check and verify that VNC server is listening
netstat -tlnp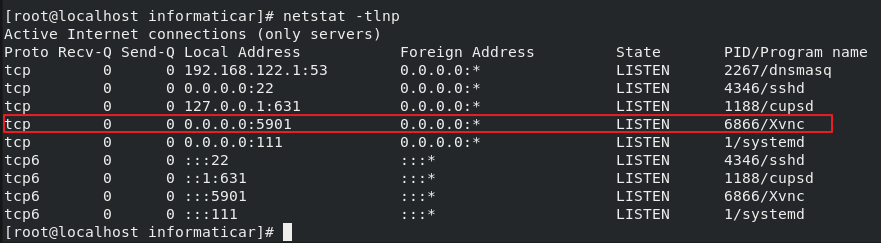
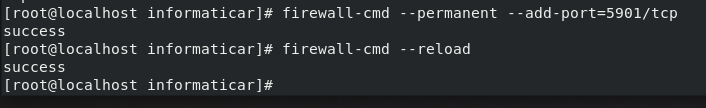
Next, we will add VNC port exceptions to firewall. We will open port 5901
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=5901/tcp
firewall-cmd –reload
We will now try and connect to our VNC server via Windows client. One thing that is important and worth mentioning – VNC is not secure by itself, and it is completely unencrypted. SSL tunneling is preferred method of connecting to VNC, but more on that in other article.
Right now, let’s just test VNC with VNC viewer – it works!