NTP server is important component in every enterprise system since it gets the network time synchronized, scripts execute on time, backup jobs done…
On RHEL 8 ntp is implemented by chronyd. Chrony can work both as server and client.
So, let us set it up.
(run all commands as root)
Install and configure chrony server:
First, we will install the package
sudo yum -y install chrony
Next, we will start chronyd service and set it to start after reboot
systemctl start chronyd
systemctl status chronyd
systemctl enable chronyd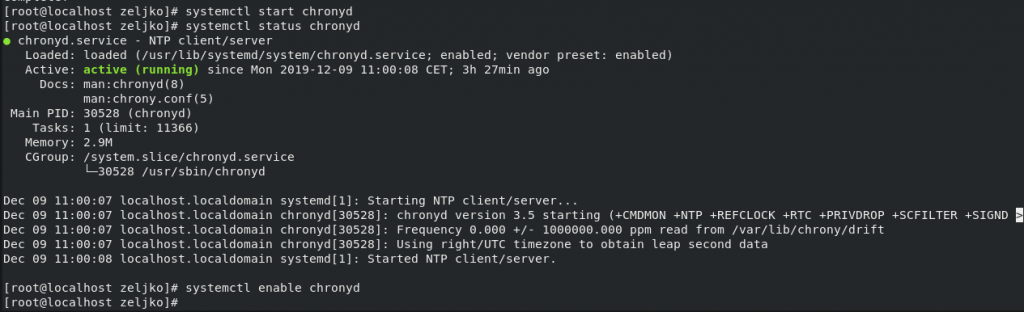
Now we will set Chrony as our main time server for the local network.
We will edit /etc/chrony.conf
I will edit it with vi editor.
vi /etc/chrony.conf
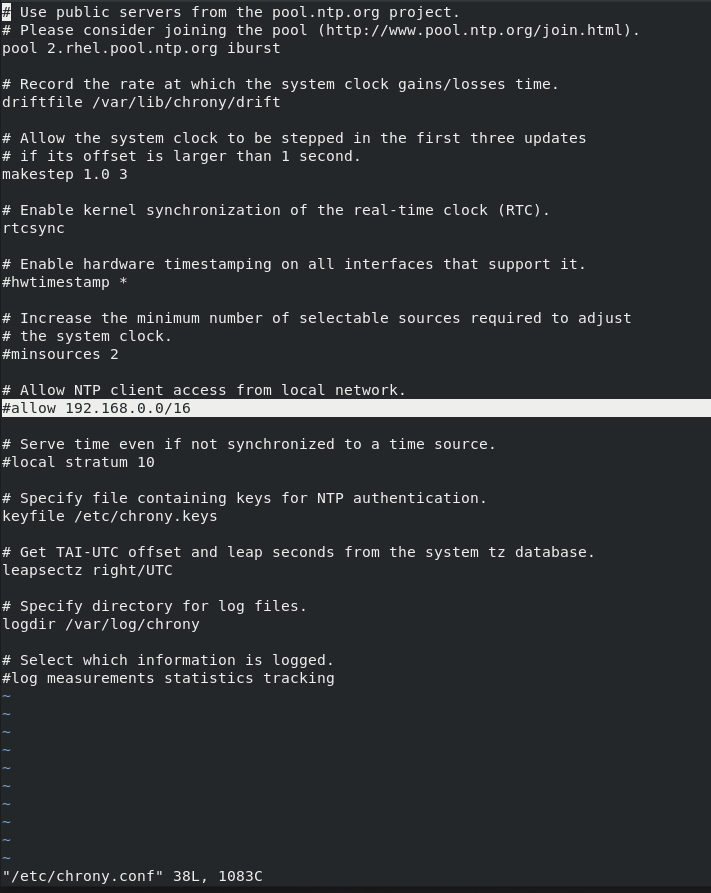
There is a line in chrony.conf which we will uncomment and set to allow machines from local network to update from our time server
Before
I will set network for my lab network, you of course will enter network you use
This is after
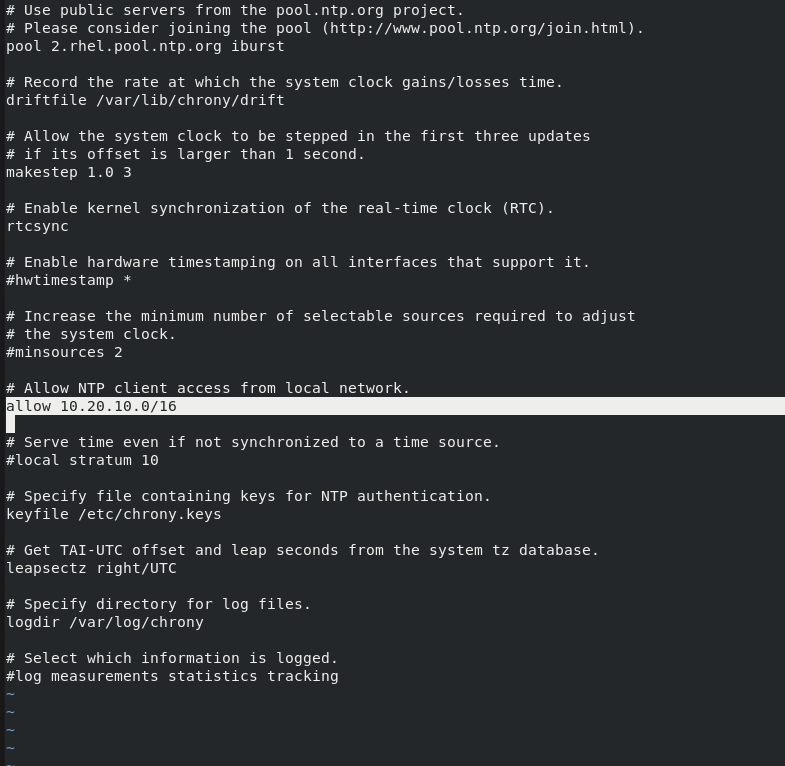
Save and exit
You can also use /etc/chrony.conf file to add more NTP servers to it, here are some of the NTP servers you can add:
server 0.rhel.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 1.rhel.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 2.rhel.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 3.rhel.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 0.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 1.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 2.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 3.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
here is also great list of NTP servers here – https://www.ntppool.org/en/
I added a few servers that are close to my area – at the beginning of the /etc/chrony.conf
Save and exit…
After that we can run following command
sudo timedatectl set-ntp true
Restart service by entering:
systemctl restart chronyd
Next, we will open firewall to allow NTP requests
(two minuses are before permanent, add and reload words)
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=ntp
firewall-cmd --reload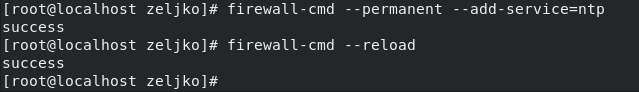
We will now check if NTP is working by entering following command
chronyc sources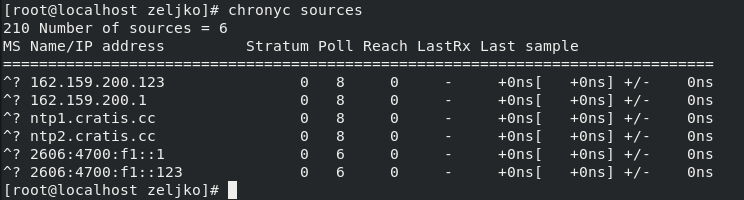
Now, we will set client to sync time with our NTP server.
I have CentOS 8 which will serve as a client for this purpose
Frist, we will install chrony to our client
yum install chrony
In my case it is already installed, but you will confirm you want to install if you don’t have installation.
Next step will be to start and enable chrony service after reboot
systemctl start chronyd
systemctl enable chronyd
systemctl status chronyd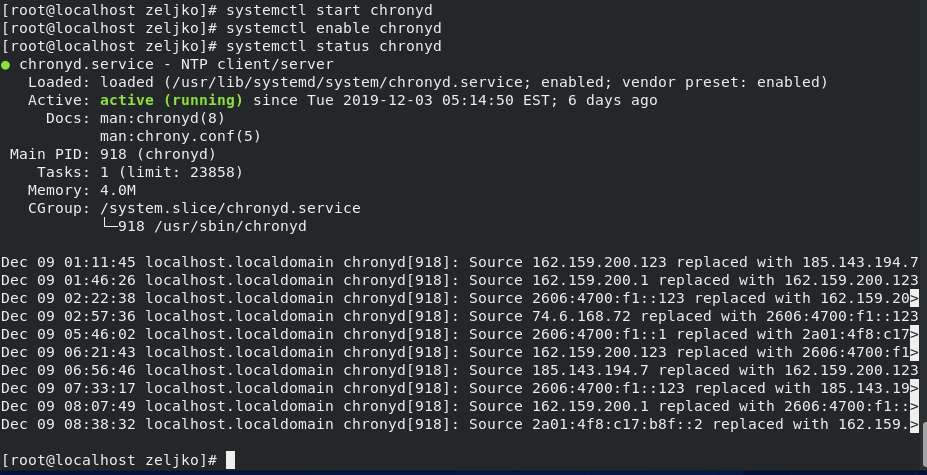
Again, we will edit /etc/chrony.conf again, this time on this client
vi /etc/chrony.conf
Comment ntp servers that are active at the top of the document and enter address of your local ntp server. In my case it is
server 10.20.10.7
It should look like this
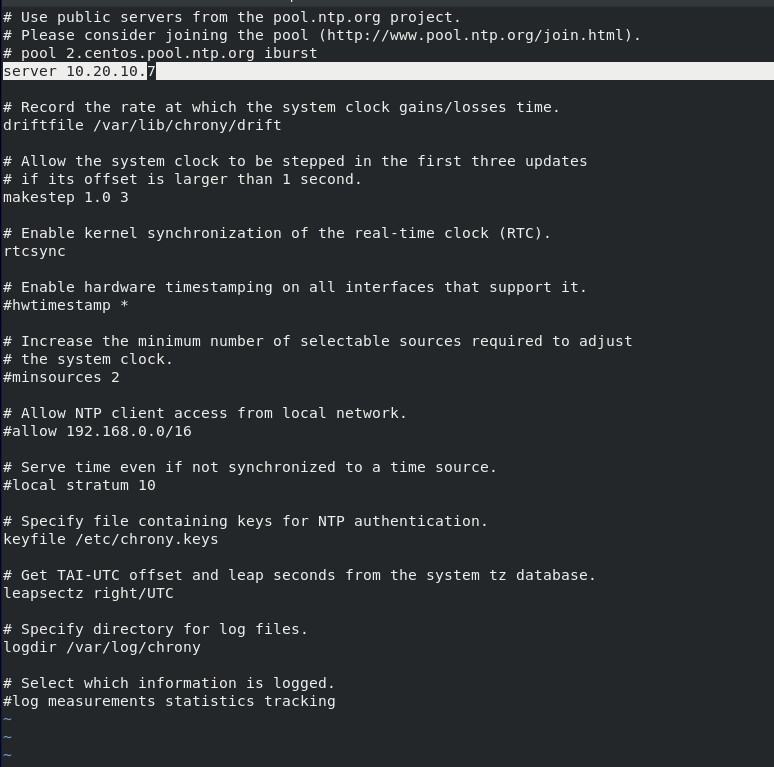
Save and exit
Set NTP synchronization by entering:
sudo timedatectl set-ntp true
Now, we will restart chronyd service by entering:
systemctl restart chronyd
On client, check to see what are your ntp servers by entering:
chronyc sources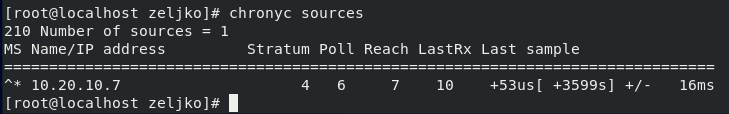
On server, you can check active clients by entering
chronyc clients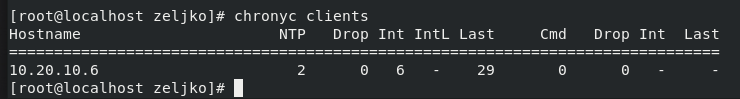
In case you are getting question mark instead of *, check again your settings, check firewall setup, check if the chrony service is active on server and client, recheck all.